Overloading vs Overriding in Java: Key Differences
Updated on : 22 MAY 2025

Image Source: google.com
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Understanding Static Methods in Java
- 3. What is Method Overriding
- 4. What is Method overloading
- 5. Can Static Methods Be Overridden in Java
- 6. Can You Overload Static Methods
- 7. Key Differences Between Overloading and Overriding
- 8. Static vs Non-Static Methods: A Comparison
- 9. Real-life Examples of Method Overloading
- 10. Practical Use Cases of Method Overriding
- 11. How JVM Handles Static and Overridden Methods
- 12. Common Errors in Overloading and Overriding
- 13. FAQs
Table Of Contents
Introduction
Overloading vs Overriding in Java: Key Differences Think of overloading as giving the same tool different powers based on the job, while overriding replaces old behavior with new tricks. Mastering Overloading vs Overriding in Java: Key Differences unlocks cleaner, smarter, and more flexible code!
Understanding Static Methods in Java
🔹 Key Points:
- ✅ Defined using
statickeyword – runs without creating an object. - 📦 Shared among all instances – only one copy exists.
- 🚫 Cannot access non-static data directly – needs an object for that.
- ⚙️ Common in utility/helper classes – like
Math.pow().
🔍 Real Example:
class Utility {
static int square(int x) {
return x * x;
}
}Use it like: Utility.square(5);
💡 Related Concept:
In Overloading vs Overriding in Java: Key Differences, static methods can be overloaded, but not overridden (technically it’s method hiding). This is an important concept in understanding Overloading vs Overriding in Java: Key Differences.
What is Method Overriding
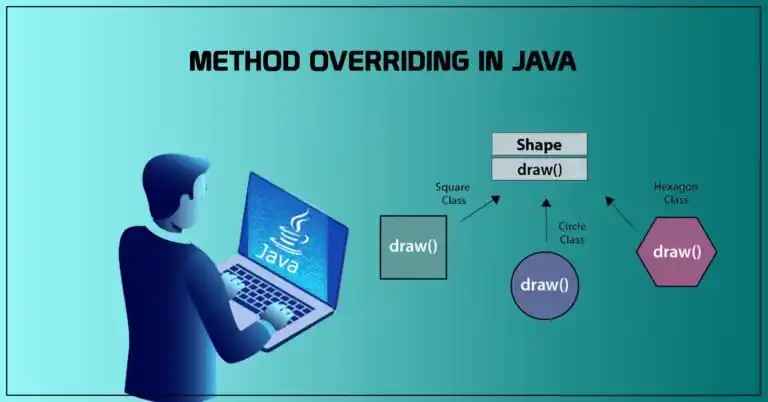
Image Source: google
| 🔍 Aspect | 📝 Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Method Overriding means redefining a superclass method in a subclass with the same name, return type, and parameters |
| Inheritance | Only occurs in inheritance (parent-child relationship) |
| Runtime Polymorphism | Supports runtime polymorphism, allowing dynamic method calls |
| Access Modifiers | Overridden method must have the same or more accessible modifier |
| Static Methods | Static methods cannot be overridden (they are hidden) |
| @Override Annotation | Used to indicate that a method is being overridden |
What is Method overloading

Image Source: google
| 🔍 Aspect | 📝 Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Method Overloading means defining multiple methods with the same name but different parameters (type, number, or order) |
| Compile-time Polymorphism | Achieved at compile time (also called static polymorphism) |
| Inheritance | Not required; can happen within a single class |
| Return Type | Can be same or different, but overloading is not determined by return type alone |
| Parameter Variation | Overloading depends on varying number or types of parameters |
| Usage | Improves code readability and flexibility |
Can Static Methods Be Overridden in Java
No, static methods cannot be overridden in Java. Here's a simple breakdown:
🔹 Static methods belong to the class, not to objects. 🔹 When a static method is declared in a subclass with the same name, it hides the superclass method, but does not override it. 🔹 This is known as method hiding, not overriding.
✅ Key Points:
- 🔄 Overriding applies only to non-static (instance) methods.
- 🧱 Static methods are resolved at compile-time, not run-time.
- 🚫 Polymorphism does not apply to static methods.
Overloading vs Overriding in Java: Key Differences clearly show that static methods can’t use true overriding behavior. Understanding this is crucial when mastering Overloading vs Overriding in Java: Key Differences in object-oriented programming.

Need help for Hire Java Developers?
Can You Overload Static Methods
-
Yes, you can overload static methods in Java. (Overloading means having multiple methods with the same name but different parameters.)
-
Overloading static methods works just like overloading instance methods — the method signature must differ by parameter types or number.
-
Static method overloading happens at compile-time (also called compile-time polymorphism).
-
You cannot override static methods, but you can overload them. This is an important part of Overloading vs Overriding in Java: Key Differences.
-
When calling an overloaded static method, Java decides which method to execute based on the argument types.
Quick Example 📚
class Example {
static void display() {
System.out.println("No arguments");
}
static void display(int a) {
System.out.println("One argument: " + a);
}
}Here, both display() methods are static but overloaded because their parameters differ.
Important Note on Overloading vs Overriding in Java: Key Differences 🔑
- Overloading: Same method name, different parameters, happens in the same class, can be static or instance methods.
- Overriding: Same method signature (name + parameters), in subclass, instance methods only, related to runtime polymorphism.
You Might Also Like
Key Differences Between Overloading and Overriding
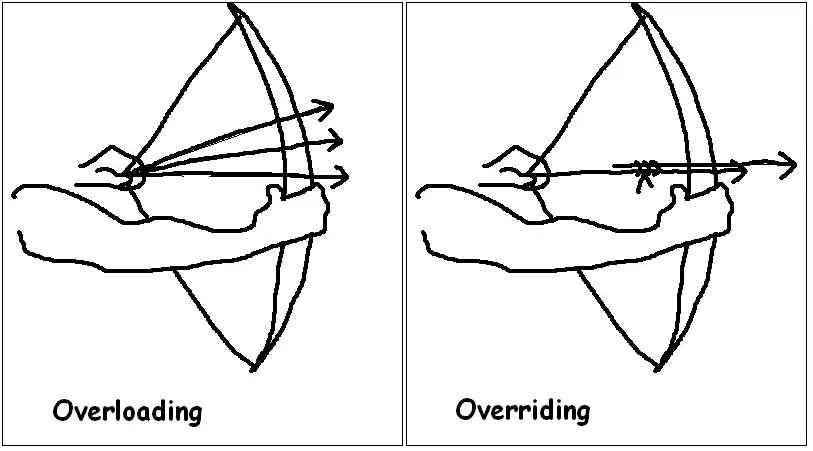
Image Source: google
| 🔍 Aspect | 📝 Overloading | 📝 Overriding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Same method name with different parameters in the same class. | Same method name and parameters in subclass, changing parent behavior. |
| When Resolved | At compile time (static binding). | At runtime (dynamic binding). |
| Inheritance Needed | No, happens within the same class. | Yes, between superclass and subclass. |
| Method Type | Can be static or instance methods. | Only instance methods (no static). |
| Return Type | Can be different but not used to distinguish methods. | Must be the same or covariant return type. |
| Purpose | Improves code flexibility and readability. | Modifies or extends the behavior of parent class methods. |
Static vs Non-Static Methods: A Comparison
| ⚙️ Aspect | 📋 Description |
|---|---|
| Belongs To | Static methods belong to the class; Non-static methods belong to instances (objects) |
| Invocation | Static methods called using class name; Non-static methods called using object reference |
| Access to Members | Static methods can only access static variables and methods; Non-static methods can access both static and instance members |
| Overriding | Static methods cannot be overridden, but can be hidden; Non-static methods can be overridden |
| Use Case | Utility or helper functions that don't require object state vs behaviors related to object state |
| Memory | Static methods have a single copy shared by all instances; Non-static methods have separate copies per object |
Real-life Examples of Method Overloading
-
What is Method Overloading? Defining multiple methods with the same name but different parameters in the same class.
-
Example 1: Calculator 🧮
-
add(int a, int b)— adds two integers -
add(double a, double b)— adds two decimal numbers -
add(int a, int b, int c)— adds three integers Same method nameadd, different parameter lists.
Example 2: Printing System 🖨️
-
print(String text)— print text message -
print(int number)— print number -
print(String text, int copies)— print multiple copies Sameprintmethod, different arguments. -
Example 3: User Registration Form 📝
-
register(String username)— register with username -
register(String username, String email)— register with username and email -
register(String username, String email, String phone)— register with more details
Summary
- Overloading helps to perform similar tasks with different inputs.
- It improves code readability and flexibility.
- Common in everyday programming like calculators, printers, and forms.

Do You Want to Hire Expert Java Developers?
Practical Use Cases of Method Overridings
| 🛠️ Use Case | 📋 Description |
|---|---|
| Polymorphism | Allow different object types to be treated uniformly through a common interface |
| Custom Behavior | Enable subclasses to provide specific implementations for inherited methods |
| Extensibility | Support extending or modifying base class functionality without changing it |
| Runtime Decision | Decide which method implementation to invoke at runtime based on object type |
| Code Reusability | Reuse base class code while overriding only the parts that need to change |
| Framework Design | Allow users to override hooks or callbacks to customize framework behavior |
How JVM Handles Static and Overridden Methods
-
Static Methods:
-
Resolved at compile-time (early binding).
-
Called using the class name, not the object.
-
JVM does not use dynamic dispatch for static methods.
-
Static methods cannot be overridden, only hidden.
-
Overridden Methods:
-
Resolved at runtime (late binding).
-
JVM uses dynamic method dispatch based on the object’s actual type.
-
Allows polymorphism where subclass method replaces the parent class method.
Common Errors in Overloading and Overriding

Image Source: google
| ⚠️ Error Type | 📝 Description |
|---|---|
| Incorrect Method Signature | Overloading requires different parameter lists; same signature causes compile errors |
| Changing Return Type | Overriding requires the same or covariant return type; changing return type causes errors |
| Static vs Non-Static | Static methods cannot be overridden; trying to override static methods causes hiding, not polymorphism |
| Access Modifier Violation | Overriding methods cannot have more restrictive access than the parent method |
| Exception Handling | Overriding methods cannot throw broader checked exceptions than the overridden method |
| Calling Superclass Methods | Failure to call super in overridden methods when required can cause logic errors |
FAQs
Q.1. What is method overloading?
A : Defining multiple methods in the same class with the same name but different parameter lists.
Q.2. What is method overriding?
A : Defining a method in a subclass with the same name, return type, and parameters as in its superclass.
Q.3. Can overloaded methods have different return types?
A : Yes, return type can be different in overloading.
Q.4. Can overridden methods have different return types?
A : No, return types must be the same or covariant (subclass type).
Q.5. Does overloading happen at compile time or runtime?
A : Compile time (also called static polymorphism).
Q.6. Does overriding happen at compile time or runtime?
A : Runtime (also called dynamic polymorphism).
Q.7. Can static methods be overridden?
A : No, static methods cannot be overridden; they can be hidden.






